Are coronavirus cases now levelling off? Daily cases average drops for first time in a fortnight and 98 deaths are recorded after ONS estimated number of infections in England has fallen 12% in a week to 3,700
- Statistics reveal 834 cases are being registered each day — down slightly from yesterday’s average of 835
- The number of patients testing positive is still much higher than the four-month low figure of 546 on July 8
- The ONS now believes there are 3,700 people in England getting infected with the coronavirus every day
- Its estimate last week was 4,200 and prompted PM Boris Johnson to pause the lifting of some measures
- Health chiefs also announced 98 more patients who tested positive for the life-threatening virus have died
- For comparison, 49 coronavirus deaths were officially recorded yesterday and 120 were declared last Friday
- Around 56 Brits are now succumbing to the infection each day — but figures show the rate has yet to spike
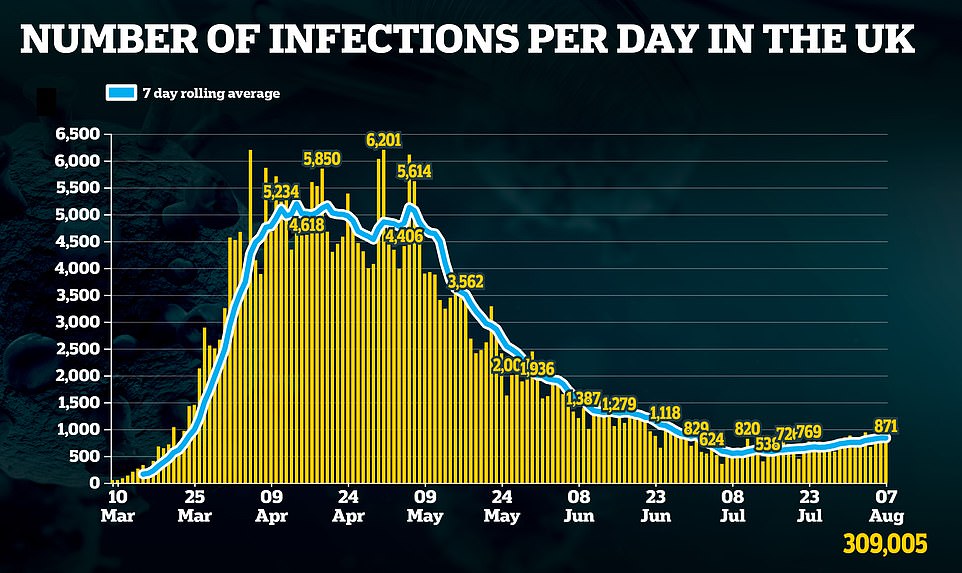
Britain today recorded another 871 Covid-19 cases as official data shows the number of people getting diagnosed with the life-threatening disease each day has dropped for the first time in a fortnight.
Department of Health statistics reveal 834 new infections are being registered each day — down slightly from the rolling seven-day average of 835 yesterday. But the number of patients testing positive daily is still much higher than the four-month low figure of 546 on July 8.
Cases have steadily risen since over the past month, fuelling fears of a second wave. But separate figures released today suggested the number of people getting infected with coronavirus in England may have actually dropped 12 per cent in a week.
The Office for National Statistics (ONS), which tracks the size of the outbreak through swab tests of thousands of people, now believes there are 3,700 people in England catching Covid-19 each day. Its estimate of 4,200 daily cases last week prompted Boris Johnson to declare he was ‘squeezing the brake pedal’ on easing the coronavirus lockdown.
Officials today also announced another 98 patients who tested positive for the infection have died — taking the official number of victims to 46,430 since the crisis spiralled out of control in February.
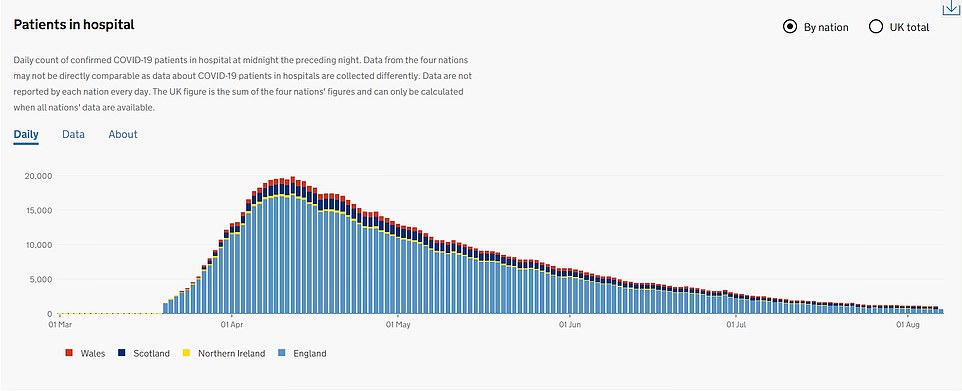
For comparison, 49 deaths were officially recorded yesterday and 120 were declared last Friday. Around 56 Brits are now succumbing to the life-threatening infection each day, on average. But the number of deaths have yet to spike and hospital admissions have remained stable, despite the rising number of cases.
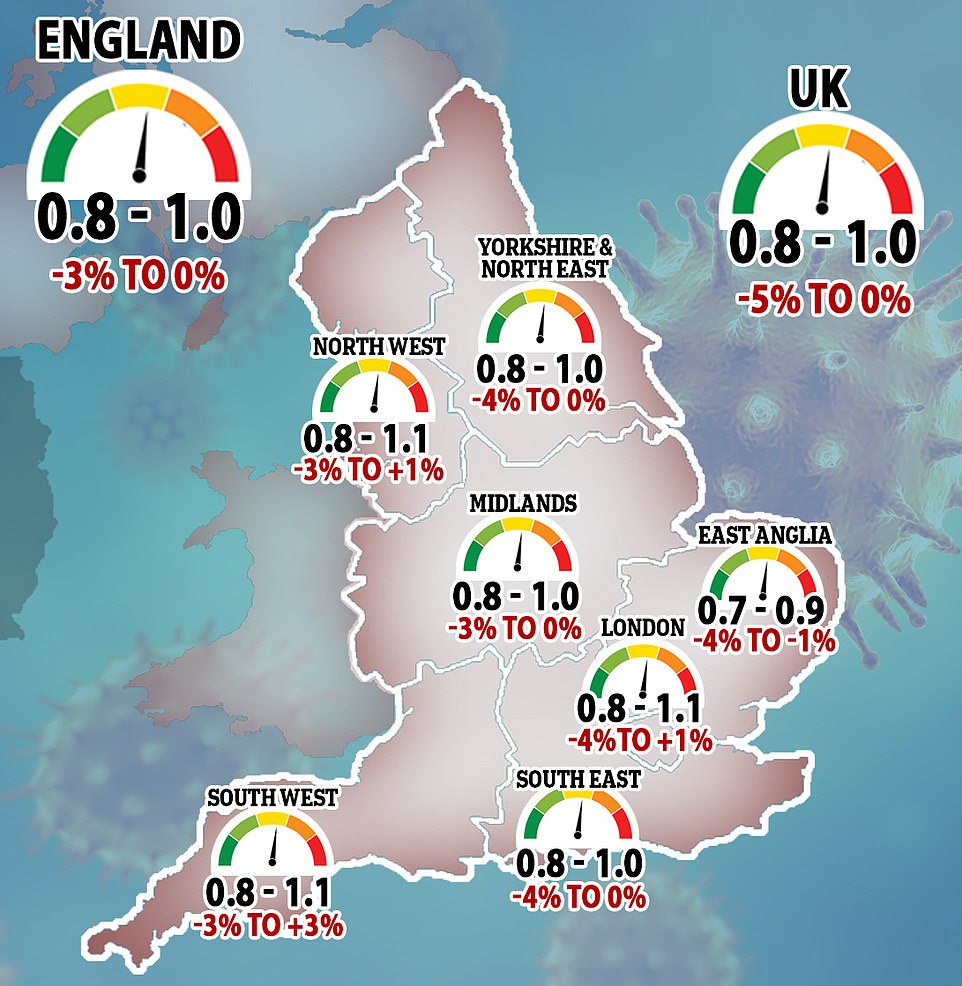
Government scientific advisers today warned the coronavirus reproduction rate could now be as high as one right across the UK. SAGE estimates the R value – the average number of people each Covid-19 patient infects – is now between 0.8 and 1.0, up from last week’s prediction that it was hovering around 0.8 and 0.9. Experts say the R needs to stay below one or Governments risk losing control of the epidemic and the virus could spiral back out of control.
In other coronavirus developments in Britain today:
- Britons were urged to stay away from packed beaches amid overcrowding fears on what could be the UK’s hottest day on record with Saharan air pushing temperatures above 100F (38C) for the second time in a week;
- Rishi Sunak delivered a stark warning to Britons that the government ‘will not hesitate’ to take action by imposing quarantine bans amid fears France could be the next holiday destination to face coronavirus curbs;
- Tory MPs have clashed with Manchester mayor Andy Burnham over his claims that it would be ‘impossible’ to lift lockdown restrictions in just one borough ahead of a review today;
- More than 100,000 people could have died from coronavirus in Britain if the government didn’t tell people to stay at home, according to research.

Department of Health chiefs yesterday announced that another 950 people tested positive for the virus, taking the rolling seven-day average to 835.
The rate has been on the up for over a fortnight amid growing fears of a resurgence, after dipping to a four-month low of 546 on July 8.
Government statistics show the official size of the UK’s outbreak now stands at 308,134. But the actual size of the outbreak is estimated to be in the millions, based on antibody testing data.
Professor Carl Heneghan, director of Oxford University’s Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine, this week claimed Covid-19 cases aren’t actually rising — despite government figures showing an upwards trend.
He said the rising infection rates are down to more people being tested, pointing to data showing the number of pillar two tests carried out each day rose by 80 per cent over the course of July to around 80,000.
The deaths data does not represent how many Covid-19 patients died within the last 24 hours — it is only how many fatalities have been reported and registered with the authorities.
And the figure does not always match updates provided by the home nations. Department of Health officials work off a different time cut-off, meaning daily updates from Scotland and Northern Ireland are out of sync.
The count announced by NHS England every afternoon, which only takes into account deaths in hospitals, does not match up with the DH figures because they work off a different recording system.
For instance, some deaths announced by NHS England bosses will have already been counted by the Department of Health, which records fatalities ‘as soon as they are available’.
NHS England today declared ten victims in hospitals across the country. Wales recorded seven in all settings. No fatalities were registered in Scotland or Northern Ireland.
But the fatality curve is no longer flattening as quickly as it was, with the rolling seven-day average number of daily deaths having been in the sixties since July 18.
It can take infected patients several weeks to die, meaning any spike in deaths won’t be immediately apparent in government figures.
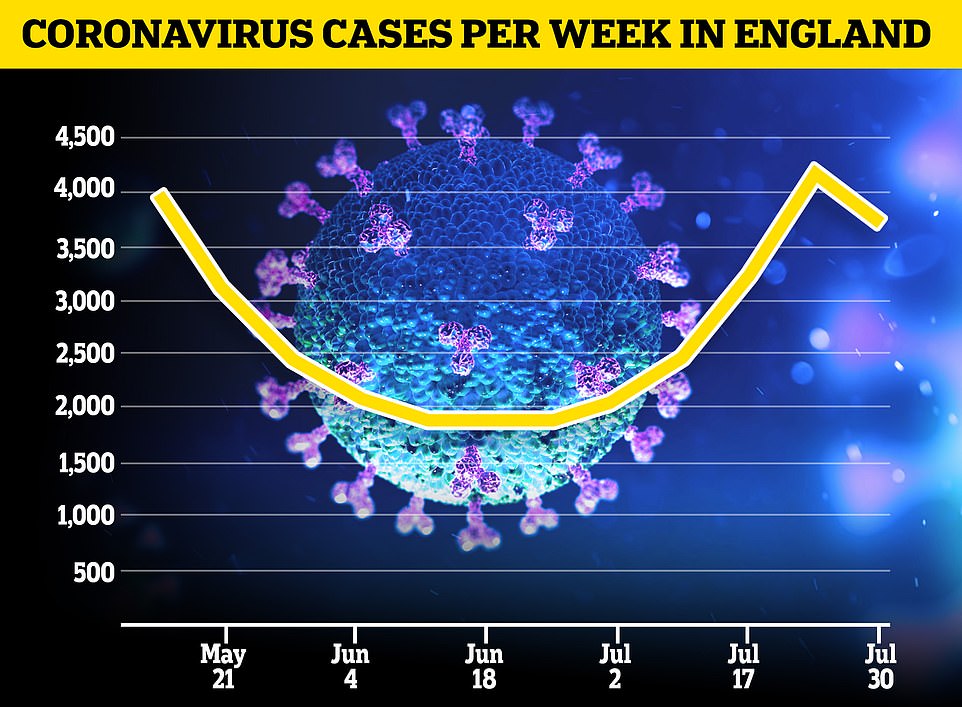
The Office for National Statistics (ONS), which tracks the size of the outbreak by swabbing thousands of people, now believes there are 3,700 people in England getting infected with Covid-19 each day. It is 12 per cent down on the 4,200 made in the government-run agency’s estimate last week, when they warned there was ‘enough evidence’ to prove cases were spiralling

SAGE estimates the R value – the average number of people each Covid-19 patient infects – is now between 0.8 and 1.0, up from last week’s prediction that it was hovering around 0.8 and 0.9
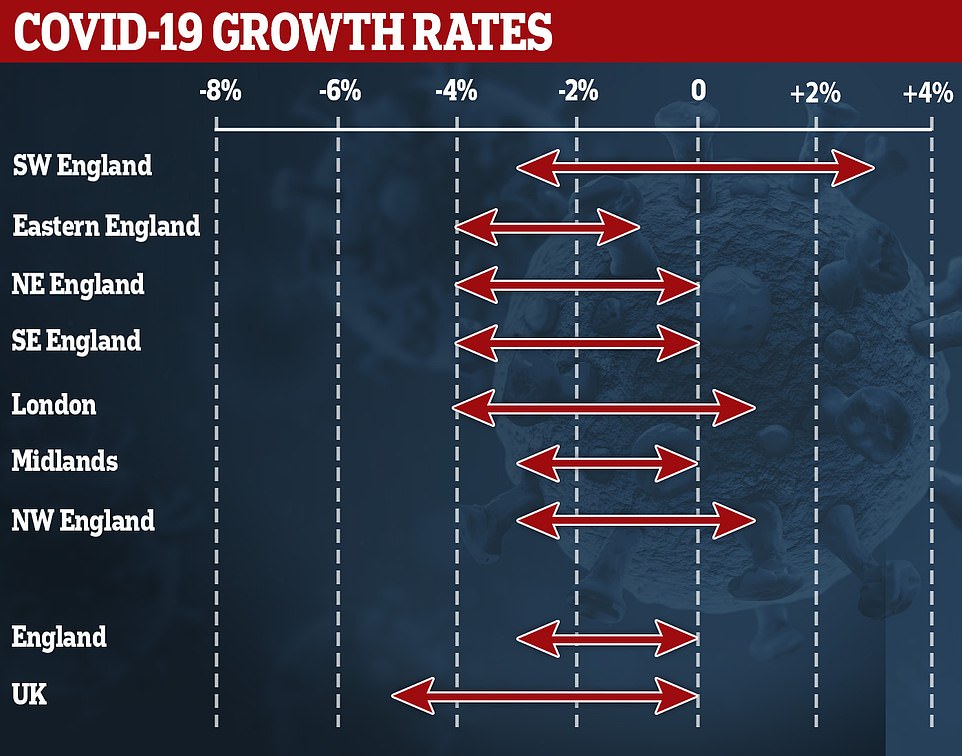
The UK’s current growth rate — how the number of new cases is changing day-by-day — is between minus five and zero per cent
It comes as the ONS today estimated 28,300 people in England had the coronavirus between July 27 and August 2 – the equivalent of one in 1,900 people. In comparison, last week’s rate was one in 1,500.
But top scientists have argued the figures are not proof of a second wave and are merely down to an increase in testing in areas that have been hit by flare-ups of the disease.
The coronavirus reproduction rate could now be as high as one right across the UK after rising slightly in the last week, the Government’s scientific advisers warned today amid fears the virus is making a resurgence.
SAGE also estimates the R value – the average number of people each Covid-19 patient infects – is now between 0.8 and 1.0, up from last week’s prediction that it was hovering around 0.8 and 0.9.
Experts say the R needs to stay below one or Governments risk losing control of the epidemic and the virus could spiral back out of control.
England as a whole has remained the same at 0.8 to 1.0, but the R rose in Scotland (0.6 and 1.0), Wales (0.7 and 1.0), Northern Ireland (0.8 and 1.8), London (0.8 and 1.1), the North East and Yorkshire (0.8 and 1.0), and in the Midlands (0.8 and 1.0).
The East of England is the only region in the entire UK where scientists can say with certainty that the R is below one.
SAGE said it was now ‘starting to see early indications that’ coronavirus was on the rise, which has fuelled fears that a second wave of the virus is making its way through the country.
But it warned that when transmission is as low as it currently is in the UK – less than 1,000 people are being diagnosed every day – the R is more volatile.
This means it can be skewed upwards by local clusters of infections, which has been seen in Aberdeen in Scotland and in swathes of the North West of England.